Value Creation
Apple's Success Story
Aug 23, 2024

How did Apple become one of the most valuable companies in recent history? Apple's success story is one of the most inspiring tales in corporate history and has captivated the world’s attention for more than four decades. From near bankruptcy in the 1990s to the pinnacle of the high-tech industry, Apple Inc's journey to becoming a multi-trillion-dollar company is nothing short of remarkable.
While there is not a single strategy that could be credited for all this success, Apple made some great strategic choices over the same period which combined with superb execution created a tremendous amount of value. In this blog post, we will explore some of those key strategies that drove Apple's remarkable growth over time.
Innovative business practices that enabled growth and success
When it comes to product innovation and business practices, Apple is a major player in the game. The company has built its success on a series of groundbreaking and frequently disruptive products that have had a massive impact on the way we live our daily lives. Apple's sleek and simple designs, coupled with their focus on making the best products in the world, have created significant delight and perceived value among their customer base. This willingness to pay a premium for Apple products reflects the company's ability to not just respond to market needs, but also to create entirely new market segments. All of this has resulted in tremendous value creation for the company, reflected in its status as the #1 market-capitalized company in the world.
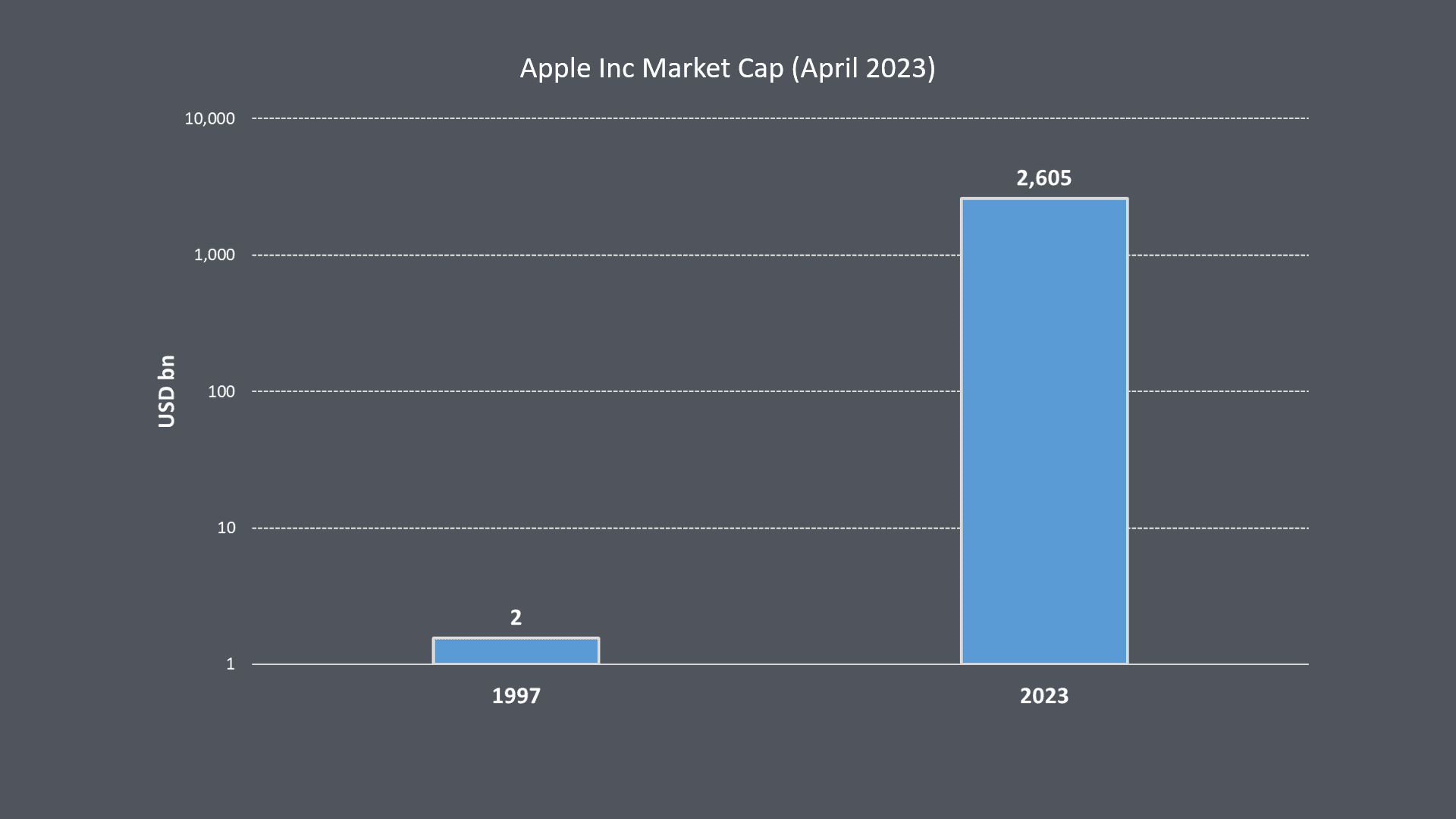
It's clear that Apple's innovative business practices and focus on timely and disruptive product design have enabled its growth and success.
iPod and iPhone
In 2001, the world of music changed forever with the launch of the iPod. This sleek and minimalist device allowed users to carry thousands of songs in their pockets, giving them unprecedented access to their favourite tunes. However, it wasn't just the device's superior design that made it so revolutionary. It was the combination of the iPod and iTunes that completely disrupted the music industry. Thanks to this innovative business model, users were able to consume media in a whole new way, making the iPod not just a music gadget, but an all-in-one media consumption device. It's hard to imagine a world without the iPod and its impact on music, which has only continued to grow since its inception.
The significance of the iPhone on the mobile device market is undeniable. It revolutionised the way we use technology and transformed it into an integral part of our daily lives. Before the iPhone, we were constrained by the need for a desktop computer or laptop to access the internet, social media, and our emails. The iPhone changed all that, with its simple design, easy-to-use interface and an internet connection available in our pockets at all times. More than a decade later, it's hard to imagine a world where we don't have this kind of access to information and connectivity. With the iPhone leading the way, the mobile device market has adapted and evolved, continually pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
How Steve Jobs started the innovation engine
Apple's innovation success did not come out of thin air. It is largely due to the way how the company is organized internally.
When Steve Jobs returned to Apple in 1997, he made some key organizational changes that live with the company up until this day. Jobs believed that the conventional business structure of separate business units had stifled innovation, so he laid off general managers and organized Apple as a functional organization with one P&L responsibility.
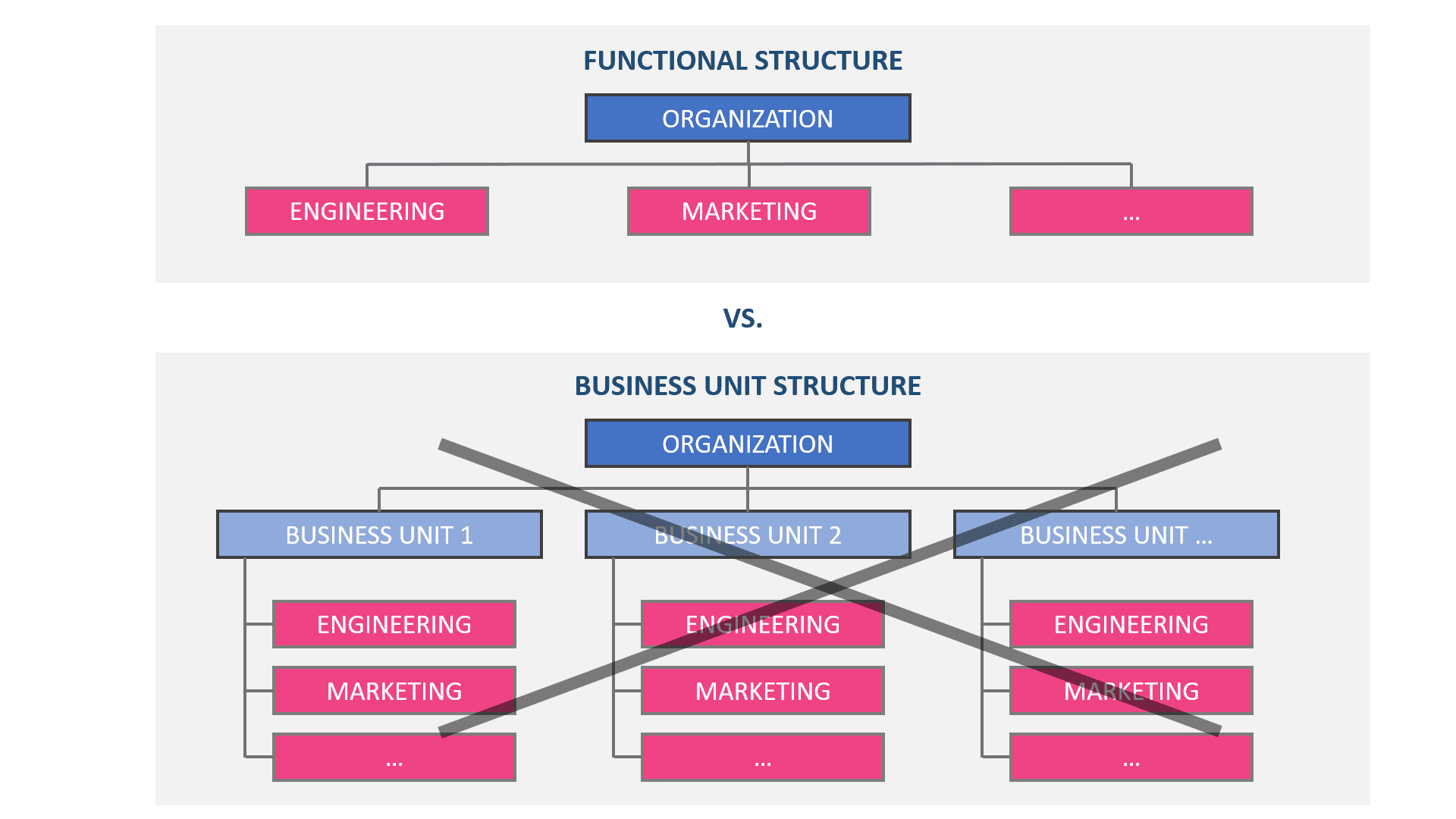
However, it is highly unusual for companies to remain organized this way, especially after they have grown above a certain size, and for Apple today which employs more than 160,000 globally. Why is Apple organized this way and how it helps its innovation capabilities? This is all because of their principal belief that the decision rights for certain domains should remain with the people who are the most experienced experts in those domains. And expertise aligns well with functions, not products or divisions. Someone is an expert in marketing, product development, or design, and not in, say, personal computers, mobile phones, or tablets.
Thus, the key to Apple's success is its organizational ability to engage resources in an innovative way that promotes alignment of expertise and decision rights. This runs in contrast to conventional wisdom where the alignment of accountability and control is the primary objective. This approach enables Apple to maintain its edge in innovation, resulting in the groundbreaking products we know today.
Complements as another key strategy
The complements strategy is another key way in which Apple creates value for their products and services.
Complements refer to products or services that increase the willingness to pay for another product or service. For example, the charging infrastructure complements electric cars, while applications complement smartphones. However, complements can also be competitors when it comes to value sharing, each striving to lower the price of the other.
Apple is a company that has utilized the complements strategy effectively. iTunes is complementary to all of its portable devices, while Apple Store is complementary to iPhone and iPad, enhancing their value. When iTunes and Apple Store were first launched in 2001 and 2008, respectively, they generated little if any direct profit for the company. Their main utility at the time was to increase the value, and thus the selling prices and profit, of their hardware products - iPod, iPhone, and iPad. At that time Apple faced limited competition on the hardware side which allowed them to be successful with this strategy.
However, with time the competitive landscape on the hardware side changed and there were an ever-increasing number of competitors offering products of similar quality to, say, the iPhone. How did Apple respond in that situation? Apple gradually shifted the value from its hardware products to the Apple Store. Over time the gross margins of iPhones dropped due to competitive pressures, but the gross margins of the Apple Store substantially increased ever since. Why was Apple able to do this? Because it owed the complement to its main product and, thus, was able to shift the profit pools in the face of competitive pressures.
Having complements in-house is of great strategic importance as it gives companies an advantage in optimizing strategic responses to increasing competition.
-----
Apple’s legacy of unparalleled innovation and inspiringly clever leadership continues to set the bar for companies all over the world. Rather than simply using traditional business methods, they have taken risks and built trust in their customers by focusing on unique marketing strategies, developing innovative products and services, and fostering meaningful relationships. It is this combination of strategies that has earned Apple its place as one of the premier technology companies of our time. When it comes to innovating solutions for the future, there is no doubt that Apple will continue to find success with its loyal fans around the world.
***
References / useful reading:
Joel M. Podolny, Morten T. Hansen: "How Apple Is Organized for Innovation", Harvard Business Review (November-December 2020), https://hbr.org/2020/11/how-apple-is-organized-for-innovation
Felix Oberholzer-Gee: "Eliminate Strategic Overload: How to select fewer initiatives with greater impact", Harvard Business Review (May-June 2021), https://hbr.org/2021/05/eliminate-strategic-overload